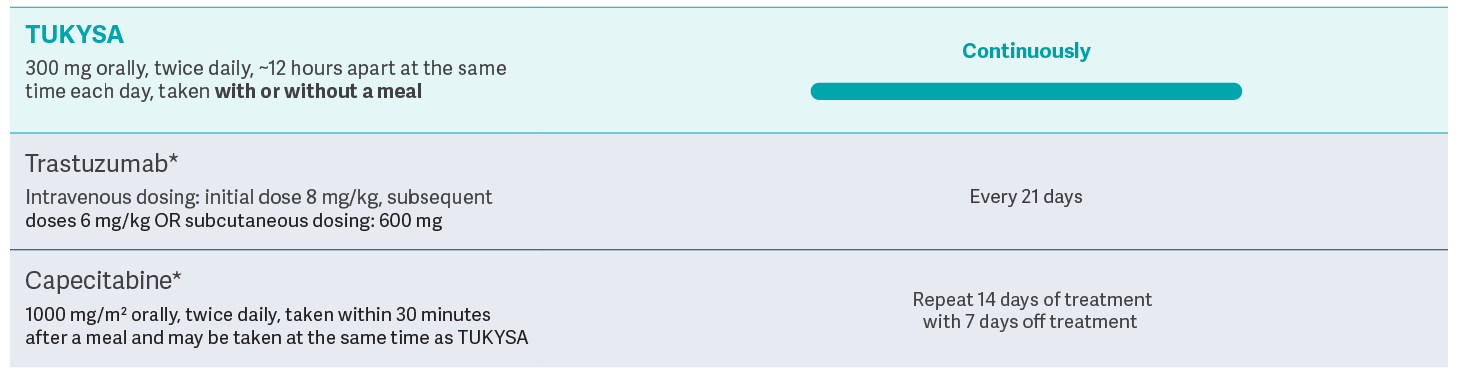
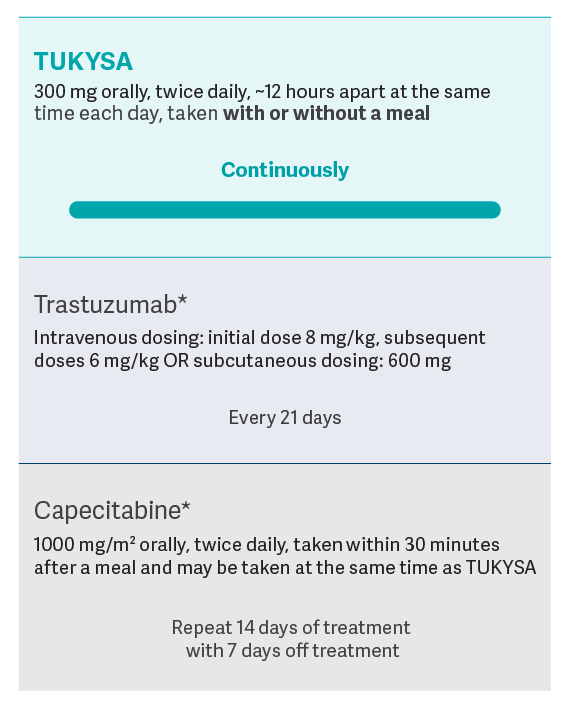
As a part of a regimen containing trastuzumab and capecitabine
TUKYSA is an oral medication taken twice a day, every day1
Dosing of TUKYSA (tucatinib) should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
*Refer to full Prescribing Information for trastuzumab and capecitabine for dose
modifications.
Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin before starting treatment, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as clinically indicated.
Additional dosing and administration
information1
- For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), the recommended starting dose of TUKYSA is 200 mg orally, twice daily
- Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP2C8 inhibitors with TUKYSA. If concomitant use with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the recommended dosage to 100 mg orally, twice daily. After discontinuation of the strong CYP2C8 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, resume the TUKYSA dose that was taken prior to initiating the inhibitor
- TUKYSA tablets should be swallowed whole; they should not be chewed, crushed, or split prior to swallowing
- If the patient vomits or misses a dose of TUKYSA, the next dose should be taken at the regularly scheduled time
- Please refer to the full Prescribing Information to learn how to modify the dose for select adverse reactions associated with TUKYSA
Dispense TUKYSA to patient in original container only. Store in original container to protect
from moisture. Replace cap securely each time after opening. Do not discard desiccant.
ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase.
TUKYSA dose modifications for adverse reactions1
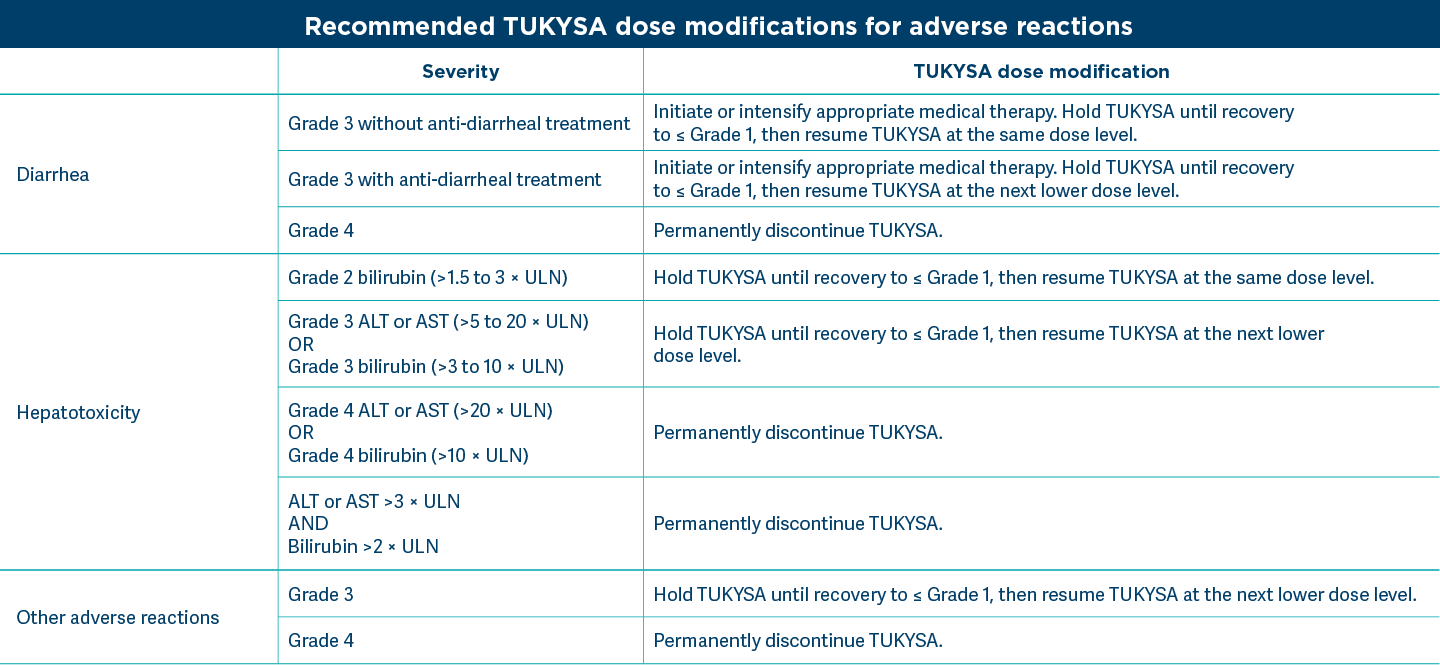
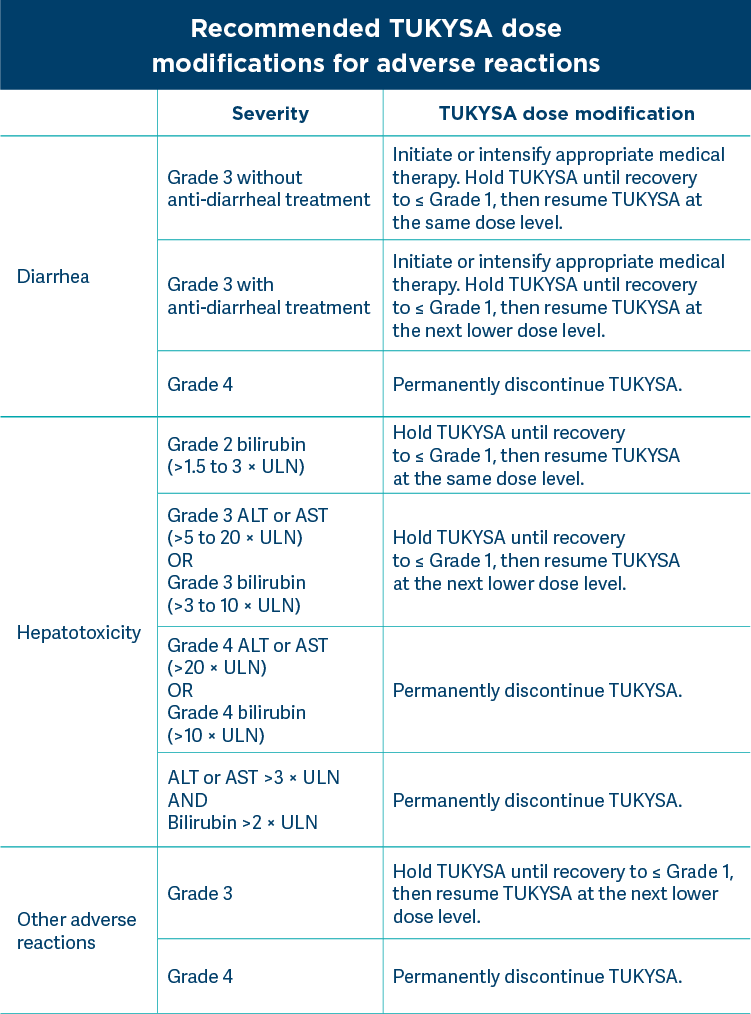
Grades based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03.
ULN = upper limit of normal.
Modifying the TUKYSA dose1
Reduce TUKYSA in increments of 50 mg to manage adverse reactions
Reduce TUKYSA in increments of 50 mg to manage adverse reactions
Recommended starting dose
First dose reduction
Second dose reduction
Third dose reduction
- Some patients may require dose modifications or discontinuations of therapy to manage adverse reactions
- In HER2CLIMB, 21% of patients had their TUKYSA dose modified and 6% permanently discontinued TUKYSA
- Permanently discontinue TUKYSA in patients unable to tolerate 150 mg orally, twice daily
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
-
Diarrhea: TUKYSA can cause severe diarrhea including
dehydration, hypotension, acute kidney injury, and death. If diarrhea
occurs, administer antidiarrheal treatment as clinically indicated.
Perform diagnostic tests as clinically indicated to exclude other
causes of diarrhea. Based on the severity of the diarrhea, interrupt
dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, when TUKYSA was given in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine, 81% of patients who received TUKYSA experienced diarrhea, including 0.5% with Grade 4 and 12% with Grade 3. Both patients who developed Grade 4 diarrhea subsequently died, with diarrhea as a contributor to death. Median time to onset of the first episode of diarrhea was 12 days and the median time to resolution was 8 days. Diarrhea led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 6% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1% of patients. Prophylactic use of antidiarrheal treatment was not required on HER2CLIMB. -
Hepatotoxicity: TUKYSA can cause severe
hepatotoxicity. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to starting
TUKYSA, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as clinically indicated.
Based on the severity of hepatotoxicity, interrupt dose, then dose
reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, 8% of patients who received TUKYSA had an ALT increase >5 × ULN, 6% had an AST increase >5 × ULN, and 1.5% had a bilirubin increase >3 × ULN (Grade ≥3). Hepatotoxicity led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 8% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1.5% of patients. - Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: TUKYSA can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential, and male patients with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during TUKYSA treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Adverse Reactions
In HER2CLIMB, serious adverse reactions occurred in 26% of patients
who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of patients) were
diarrhea (4%), vomiting (2.5%), nausea (2%), abdominal pain (2%), and
seizure (2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2% of patients who
received TUKYSA including sudden death, sepsis, dehydration, and
cardiogenic shock.
Adverse reactions led to treatment discontinuation in 6% of patients
who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥1% of patients) were
hepatotoxicity (1.5%) and diarrhea (1%). Adverse reactions led to dose
reduction in 21% of patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in
≥2% of patients) were hepatotoxicity (8%) and diarrhea (6%).
The most common adverse reactions in patients who received TUKYSA
(≥20%) were diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, nausea,
hepatotoxicity, vomiting, stomatitis, decreased appetite, anemia, and
rash.
Lab Abnormalities
In HER2CLIMB, Grade ≥3 laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥5% of patients who received TUKYSA were decreased phosphate, increased ALT, decreased potassium, and increased AST.
The mean increase in serum creatinine was 32% within the first 21 days of treatment with TUKYSA. The serum creatinine increases persisted throughout treatment and were reversible upon treatment completion. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A/Moderate CYP2C8 Inducers: Concomitant use may decrease TUKYSA activity. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA.
- Strong or Moderate CYP2C8 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of TUKYSA with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor may increase the risk of TUKYSA toxicity; avoid concomitant use. Increase monitoring for TUKYSA toxicity with moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors.
- CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a CYP3A substrate. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If concomitant use is unavoidable, decrease the CYP3A substrate dosage.
- P-gp Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a P-gp substrate. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicity.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed while taking TUKYSA and for 1 week after the last dose.
- Renal Impairment: Use of TUKYSA in combination with capecitabine and trastuzumab is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), because capecitabine is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the dose of TUKYSA for patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
REF-T1K1161
Indication
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information + Indication
Indication
Warnings and Precautions
Warnings and Precautions
-
Diarrhea:
TUKYSA can cause severe diarrhea including dehydration,
hypotension, acute kidney injury, and death. If diarrhea occurs,
administer antidiarrheal treatment as clinically indicated.
Perform diagnostic tests as clinically indicated to exclude other
causes of diarrhea. Based on the severity of the diarrhea,
interrupt dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue
TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, when TUKYSA was given in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine, 81% of patients who received TUKYSA experienced diarrhea, including 0.5% with Grade 4 and 12% with Grade 3. Both patients who developed Grade 4 diarrhea subsequently died, with diarrhea as a contributor to death. Median time to onset of the first episode of diarrhea was 12 days and the median time to resolution was 8 days. Diarrhea led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 6% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1% of patients. Prophylactic use of antidiarrheal treatment was not required on HER2CLIMB. -
Hepatotoxicity:
TUKYSA can cause severe hepatotoxicity. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to starting TUKYSA, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Based on the severity of hepatotoxicity, interrupt dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, 8% of patients who received TUKYSA had an ALT increase >5 × ULN, 6% had an AST increase >5 × ULN, and 1.5% had a bilirubin increase >3 × ULN (Grade ≥3). Hepatotoxicity led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 8% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1.5% of patients.
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity:
TUKYSA can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential, and male patients with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during TUKYSA treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Adverse Reactions
In HER2CLIMB, serious adverse reactions occurred in 26% of
patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of
patients) were diarrhea (4%), vomiting (2.5%), nausea (2%),
abdominal pain (2%), and seizure (2%). Fatal adverse reactions
occurred in 2% of patients who received TUKYSA including sudden
death, sepsis, dehydration, and cardiogenic shock.
Adverse reactions led to treatment discontinuation in 6% of
patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥1% of
patients) were hepatotoxicity (1.5%) and diarrhea (1%). Adverse
reactions led to dose reduction in 21% of patients who received
TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of patients) were hepatotoxicity
(8%) and diarrhea (6%).
The most common adverse reactions in patients who received
TUKYSA (≥20%) were diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia,
nausea, hepatotoxicity, vomiting, stomatitis, decreased
appetite, anemia, and rash.
Lab Abnormalities
In HER2CLIMB, Grade ≥3 laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥5% of patients who received TUKYSA were decreased phosphate, increased ALT, decreased potassium, and increased AST.
The mean increase in serum creatinine was 32% within the first 21 days of treatment with TUKYSA. The serum creatinine increases persisted throughout treatment and were reversible upon treatment completion. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A/Moderate CYP2C8 Inducers: Concomitant use may decrease TUKYSA activity. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA.
- Strong or Moderate CYP2C8 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of TUKYSA with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor may increase the risk of TUKYSA toxicity; avoid concomitant use. Increase monitoring for TUKYSA toxicity with moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors.
- CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a CYP3A substrate. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If concomitant use is unavoidable, decrease the CYP3A substrate dosage.
- P-gp Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a P-gp substrate. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicity.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed while taking TUKYSA and for 1 week after the last dose.
- Renal Impairment: Use of TUKYSA in combination with capecitabine and trastuzumab is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), because capecitabine is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the dose of TUKYSA for patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
REF-T1K1161
Indication
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
1. TUKYSA. Prescribing information. Seagen Inc.; 2023.

